Frequency
Been spending a lot of time on here!
- Joined
- Oct 17, 2010
- Messages
- 8,864
- Reaction score
- 683
- Location
- Calicut, Kerala,India
- Website
- www.photosenzitive.com
- Can others edit my Photos
- Photos OK to edit
This is a self learning. I am starting this. It will grow only by the contributions of experts here... I just copy and paste their contributions in the proper places. I am just an editor, not a director. This is a long term process.... Request your support
A modification:
Information in Red: basics or Very essential
Information in Green: Good to know
Information in Blue: Deep Philosophy
Regards
Latest edition on: Aperture / Bokeh/Hyper focal distance/Circle of Confusion/Diffraction/ISO/Shutter speed/Panning/Panorama/ Exposure Compensation/Aperture Priority/Shutter Priority/Front Lighting/Out of Focus/Composition/Perspective/Lens/Tripod
/Zoom/White Balance/AEB/Program Mode/Flare/Glare/Rule of Third/Prime Lens/Normal Lens/ Tele Photo Lens/Wide Angle Lens/Macro Lens/Macro Photography/Neutral density filters/Eye/Polarizing Filters/HDR/Zoom Burst/Pin Cushion Distortion/Barrel Distortion/Shutter lag/Vignetting/Shutter Mechanism/Rear Curtain Flash Synchronization/Straight Out Of Camera/Histogram/EXIF/JPEG/RAW file/Color Space/Posterization/Gray Card/Full Frame Sensor/Mirror Lock up/Bulb/Magnification/Quick Control Button/Under Exposure/ Over Exposure/High Key/Low Key Image/Light Painting/Extension Tube/ Tele Convertor/Silhouette/Noise/Blur/Rembrandt Lighting/Chiaroscuro/Key Light/Fill Light/Back Light(studio)/Rim Light/Through The Lens(Flash) Metering, TTL metering/Sweet Spot/X-ray Photography(Radiography)/Infra Red Imaging/Aspect Ratio/Bounce Lighting/Candid Photography/Contrast/Flat Image/Flat Lighting/Catch Light/Red eye Effect/ Red Eye Reduction/Parallax/Panning/Point Of Interest(POI)/Soft Box/Light Box/Patterns
Sunny 16 Rule/Negative Space/Artifacts/Batch Processing/Gel/Golden Rectangle/Digital Zoom/Backdrop/Blown out/Kicker/Dominant Object/Photogenic/Broad Light/Short Light/Monopod(Unipod)/Mask/Time Exposure/Incident light/Golden Hour (Magic Hour)/View Point/Dynamic Range/Aesthetics/ Inverse Square Law/Landscape/Leading Lines/Power line Challenge/Split Lighting/Selective Focusing/Head Shot/Recycle Time/Resolution/Key Stoning/Diopter Adjustment/Thumbnail/Burst mode(Continuous mode)/ CCD/ CMOS/ Colorcast/ Flash Assist/ Interpolation (Resampling)/ Gamma Correction/ Chromatic Aberration/Rainbow Rule
A modification:
Information in Red: basics or Very essential
Information in Green: Good to know
Information in Blue: Deep Philosophy
Regards
Latest edition on: Aperture / Bokeh/Hyper focal distance/Circle of Confusion/Diffraction/ISO/Shutter speed/Panning/Panorama/ Exposure Compensation/Aperture Priority/Shutter Priority/Front Lighting/Out of Focus/Composition/Perspective/Lens/Tripod
/Zoom/White Balance/AEB/Program Mode/Flare/Glare/Rule of Third/Prime Lens/Normal Lens/ Tele Photo Lens/Wide Angle Lens/Macro Lens/Macro Photography/Neutral density filters/Eye/Polarizing Filters/HDR/Zoom Burst/Pin Cushion Distortion/Barrel Distortion/Shutter lag/Vignetting/Shutter Mechanism/Rear Curtain Flash Synchronization/Straight Out Of Camera/Histogram/EXIF/JPEG/RAW file/Color Space/Posterization/Gray Card/Full Frame Sensor/Mirror Lock up/Bulb/Magnification/Quick Control Button/Under Exposure/ Over Exposure/High Key/Low Key Image/Light Painting/Extension Tube/ Tele Convertor/Silhouette/Noise/Blur/Rembrandt Lighting/Chiaroscuro/Key Light/Fill Light/Back Light(studio)/Rim Light/Through The Lens(Flash) Metering, TTL metering/Sweet Spot/X-ray Photography(Radiography)/Infra Red Imaging/Aspect Ratio/Bounce Lighting/Candid Photography/Contrast/Flat Image/Flat Lighting/Catch Light/Red eye Effect/ Red Eye Reduction/Parallax/Panning/Point Of Interest(POI)/Soft Box/Light Box/Patterns
Sunny 16 Rule/Negative Space/Artifacts/Batch Processing/Gel/Golden Rectangle/Digital Zoom/Backdrop/Blown out/Kicker/Dominant Object/Photogenic/Broad Light/Short Light/Monopod(Unipod)/Mask/Time Exposure/Incident light/Golden Hour (Magic Hour)/View Point/Dynamic Range/Aesthetics/ Inverse Square Law/Landscape/Leading Lines/Power line Challenge/Split Lighting/Selective Focusing/Head Shot/Recycle Time/Resolution/Key Stoning/Diopter Adjustment/Thumbnail/Burst mode(Continuous mode)/ CCD/ CMOS/ Colorcast/ Flash Assist/ Interpolation (Resampling)/ Gamma Correction/ Chromatic Aberration/Rainbow Rule
Last edited:




 a
a 



 b B
b B  b B
b B 
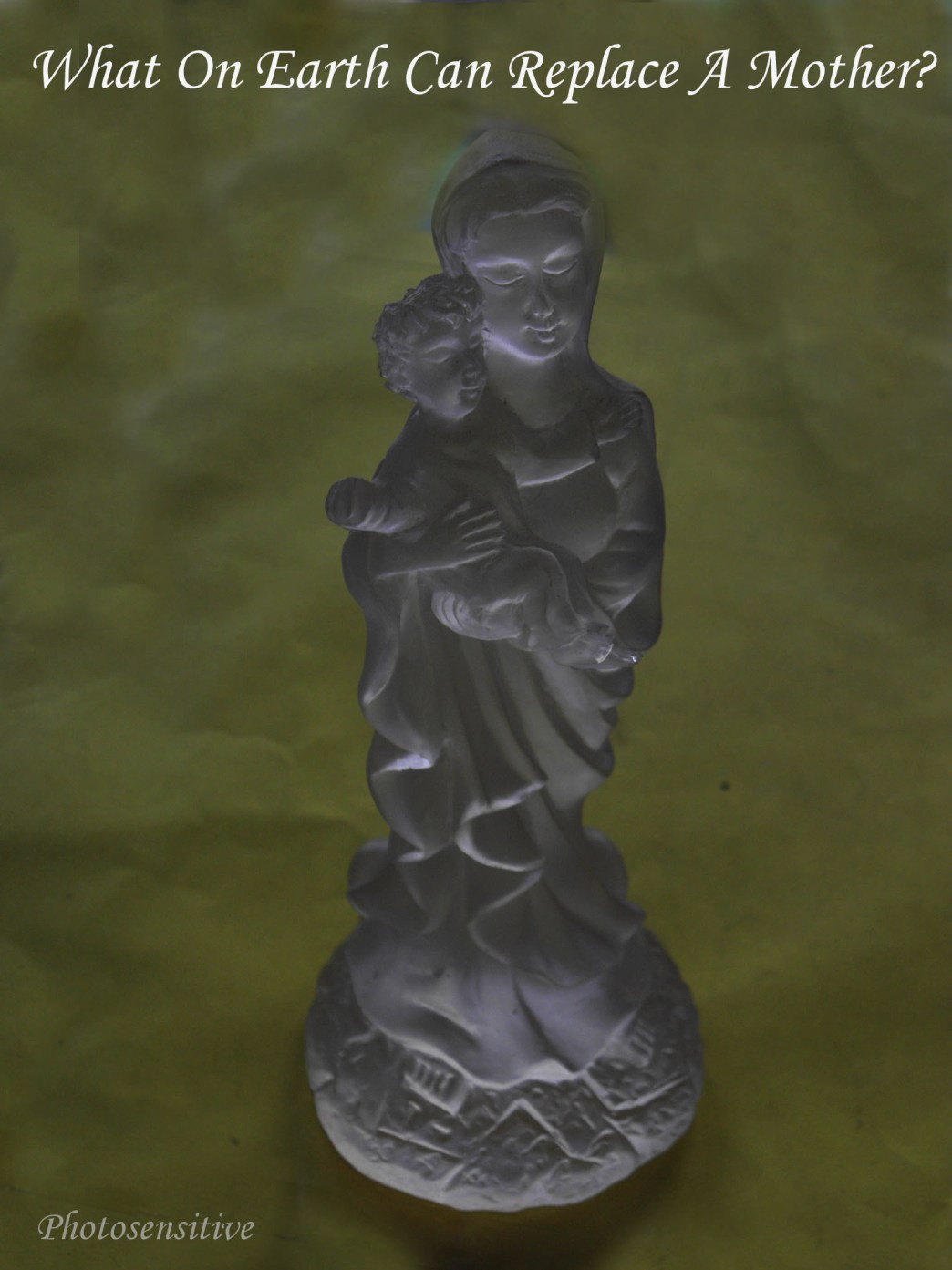


































 [/url
[/url


























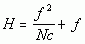
 :cheer:
:cheer:  iii :mrgreen: I
iii :mrgreen: I