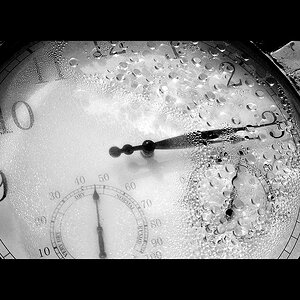
Frequency
Been spending a lot of time on here!
- Joined
- Oct 17, 2010
- Messages
- 8,864
- Reaction score
- 683
- Location
- Calicut, Kerala,India
- Website
- www.photosenzitive.com
- Can others edit my Photos
- Photos OK to edit
​N n  n N :violin:n :roll: N :angry1:n n
n N :violin:n :roll: N :angry1:n n n N :cheers: n N n
n N :cheers: n N n n
n  N n
N n  N :flower: n
N :flower: n
::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
Negative Space:​ This is an arguably wrong concept or wrongly interpreted concept. Most references found on net have pointed out the elusive or abstract nature of this idea. If the main object in the image is the positive space, the surrounding space is the negative space. In many classic images we see the vast emptiness around the main object completes the message; sometimes the space is the major object which is just accentuated by the body in it.So it is not only for emotional reasons, but even from a technical point of view the usage is not justified. More than the space it is the secondary objects that can be more distracting which may be termed negative objects.
The immediate space around the main object is the breathing space for the object. Too much of objects can make the image looks cluttered. But all these are some generalization, which definitely go wrong on many occasions. You cannot have so called breathing space in a busy market place or a crowded railway station; why, you need not necessarily have a main object there. Certain ideas are for aesthetic applications under the most ideal conditions

Technically this image has vast negative space

This image has breathing space for the subject and less or no negative space
___________________________________________________________________________________
Neutral Density Filters(ND filters): They are specially designed glass devices fitted in front of the lens to control the intensity of light entering the lens. They are either clear or tinted glasses. They have estimated absorption of the light passing through them and help to bring down the light to which the sensor is exposed.
Suppose one wants to capture an image in a bright sunny hour, but wants a slow shutter to register motion and wide aperture to minimize the depth of field. Even at the lowest ISO the image will be over exposed. Exposure compensation adjusts either shutter speed (in aperture priority mode) or aperture (in shutter priority mode) This is where a NDF is a real help. Retaining all other parameters at one's desired values one can bring down exposure to the optimum level by using NDF of appropriate stops.
NDF is generally used to enhance aperture or lower shutter speed without over exposing the image. You may say you are providing your camera lens with a cooling glass
__________________________________________________________
Graduated ND Filters: are special category filters where one half alone does the real filtering. Suppose you want to capture an image where sky is enough bright where as ground is dark due to thick green foliages and dark soil . If we adjust exposure by metering from sky, the ground details will be lost due to under exposure. Conversely If exposure is adjusted with respect to dark ground, sky will be washed out. The image thus requires two different exposures. It is in such situations, a graduated NDF is of immense help. One can keep the filtering half on the top and the other half below and adjusting exposure with respect to the ground, get proper exposure for both upper part and lower part. Gr. NDF is available with sharp demarcation between the two regions or with smooth variation.
___________________________________________________________
Noise:​In images noise is the grainy appearances, especially when the image is shot at low light conditions. Smaller sensors means less area to capture light and greater the chance of noise. For a given aperture at good lighting condition where we use lower ISO, the pixel counts per unit area or pixel density is not a deciding factor in noise development, but only the sensor size; however in low light condition where high ISO is used, greater the pixel density, more is the chance for noise. Noise has thermal reasons too. A hot day is more prone to cause noise than a normal day. One may say noise is an outcome of the struggle of the sensor to capture more light.

__________________________________________________________
Normal Lens: A lens having normal field of view compatible to human vision. Its focal length will correspond to the diagonal of the sensor. Unlike a wide angle lens or a telephoto lens, a normal lens generates no distortion to objects in the field. Usually a 50mm lens is considered as a normal lens; but (40-58)mm range is considered to fall within normal.
 n N :cheers: n N n
n N :cheers: n N n n
n  N n
N n  N :flower: n
N :flower: n::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
Negative Space:​ This is an arguably wrong concept or wrongly interpreted concept. Most references found on net have pointed out the elusive or abstract nature of this idea. If the main object in the image is the positive space, the surrounding space is the negative space. In many classic images we see the vast emptiness around the main object completes the message; sometimes the space is the major object which is just accentuated by the body in it.So it is not only for emotional reasons, but even from a technical point of view the usage is not justified. More than the space it is the secondary objects that can be more distracting which may be termed negative objects.
The immediate space around the main object is the breathing space for the object. Too much of objects can make the image looks cluttered. But all these are some generalization, which definitely go wrong on many occasions. You cannot have so called breathing space in a busy market place or a crowded railway station; why, you need not necessarily have a main object there. Certain ideas are for aesthetic applications under the most ideal conditions

Technically this image has vast negative space

This image has breathing space for the subject and less or no negative space
___________________________________________________________________________________
Neutral Density Filters(ND filters): They are specially designed glass devices fitted in front of the lens to control the intensity of light entering the lens. They are either clear or tinted glasses. They have estimated absorption of the light passing through them and help to bring down the light to which the sensor is exposed.
Suppose one wants to capture an image in a bright sunny hour, but wants a slow shutter to register motion and wide aperture to minimize the depth of field. Even at the lowest ISO the image will be over exposed. Exposure compensation adjusts either shutter speed (in aperture priority mode) or aperture (in shutter priority mode) This is where a NDF is a real help. Retaining all other parameters at one's desired values one can bring down exposure to the optimum level by using NDF of appropriate stops.
NDF is generally used to enhance aperture or lower shutter speed without over exposing the image. You may say you are providing your camera lens with a cooling glass
__________________________________________________________
Graduated ND Filters: are special category filters where one half alone does the real filtering. Suppose you want to capture an image where sky is enough bright where as ground is dark due to thick green foliages and dark soil . If we adjust exposure by metering from sky, the ground details will be lost due to under exposure. Conversely If exposure is adjusted with respect to dark ground, sky will be washed out. The image thus requires two different exposures. It is in such situations, a graduated NDF is of immense help. One can keep the filtering half on the top and the other half below and adjusting exposure with respect to the ground, get proper exposure for both upper part and lower part. Gr. NDF is available with sharp demarcation between the two regions or with smooth variation.
___________________________________________________________
Noise:​In images noise is the grainy appearances, especially when the image is shot at low light conditions. Smaller sensors means less area to capture light and greater the chance of noise. For a given aperture at good lighting condition where we use lower ISO, the pixel counts per unit area or pixel density is not a deciding factor in noise development, but only the sensor size; however in low light condition where high ISO is used, greater the pixel density, more is the chance for noise. Noise has thermal reasons too. A hot day is more prone to cause noise than a normal day. One may say noise is an outcome of the struggle of the sensor to capture more light.

__________________________________________________________
Normal Lens: A lens having normal field of view compatible to human vision. Its focal length will correspond to the diagonal of the sensor. Unlike a wide angle lens or a telephoto lens, a normal lens generates no distortion to objects in the field. Usually a 50mm lens is considered as a normal lens; but (40-58)mm range is considered to fall within normal.
Last edited:
















































![[No title]](/data/xfmg/thumbnail/34/34145-b89ccc67a24004d6d7a9026a7395914b.jpg?1619736318)






![[No title]](/data/xfmg/thumbnail/30/30861-fee88082ba36d0c3b443492fe3f3f1cd.jpg?1619734481)